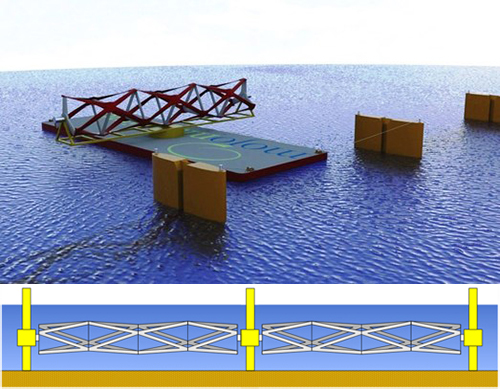
Kepler Energy’s Transverse Horizontal Axis Water Turbine (THAWT)
There are many different ways to convert tidal energy into electricity. We’ve recently come across a few innovations like the work being done at the University of Oxford (Kepler THAWT pictured above).

Seagen’s 1.2 MW Tidal Energy Converter
The LAGI 2016 design site offers an opportunity for participants to think about tidal energy technologies, their form, and their relationship to space, both above and below the surface of the water. What is the ecological impact of their addition to the sea bed?
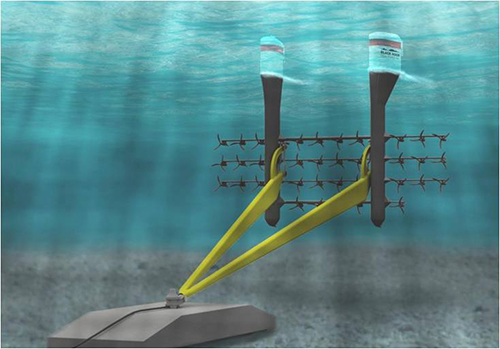

Tidal Stream Titan 1-3MW
The two major taxonomies are those that employ tidal barrage (dams) and those that catch the free-flowing tidal stream. Tidal stream type generators work very much like wind turbines, but because water is denser than air, the potential power per swept area is great.
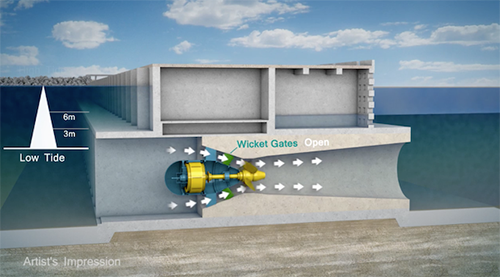
Section through the proposed Swansea Tidal Lagoon.
Check out the work that Cape Farewell is doing at Swansea.
Barrage type tidal generators—like the proposed Swansea Tidal Lagoon in Wales—tend to benefit from a sizable difference between low and high tides. It’s interesting to think of breakwater constructions and storm/sea level resiliency infrastructures as potentially serving as a tidal barrage as well.

Delta Stream by Tidal Energy
We’re looking forward to seeing what creative applications can be found that explore how this technology can be expressed with a cultural aspect.

West Islay tidal project off South West Scotland (DP Marine Energy and DEME Blue Energy Consortium)

