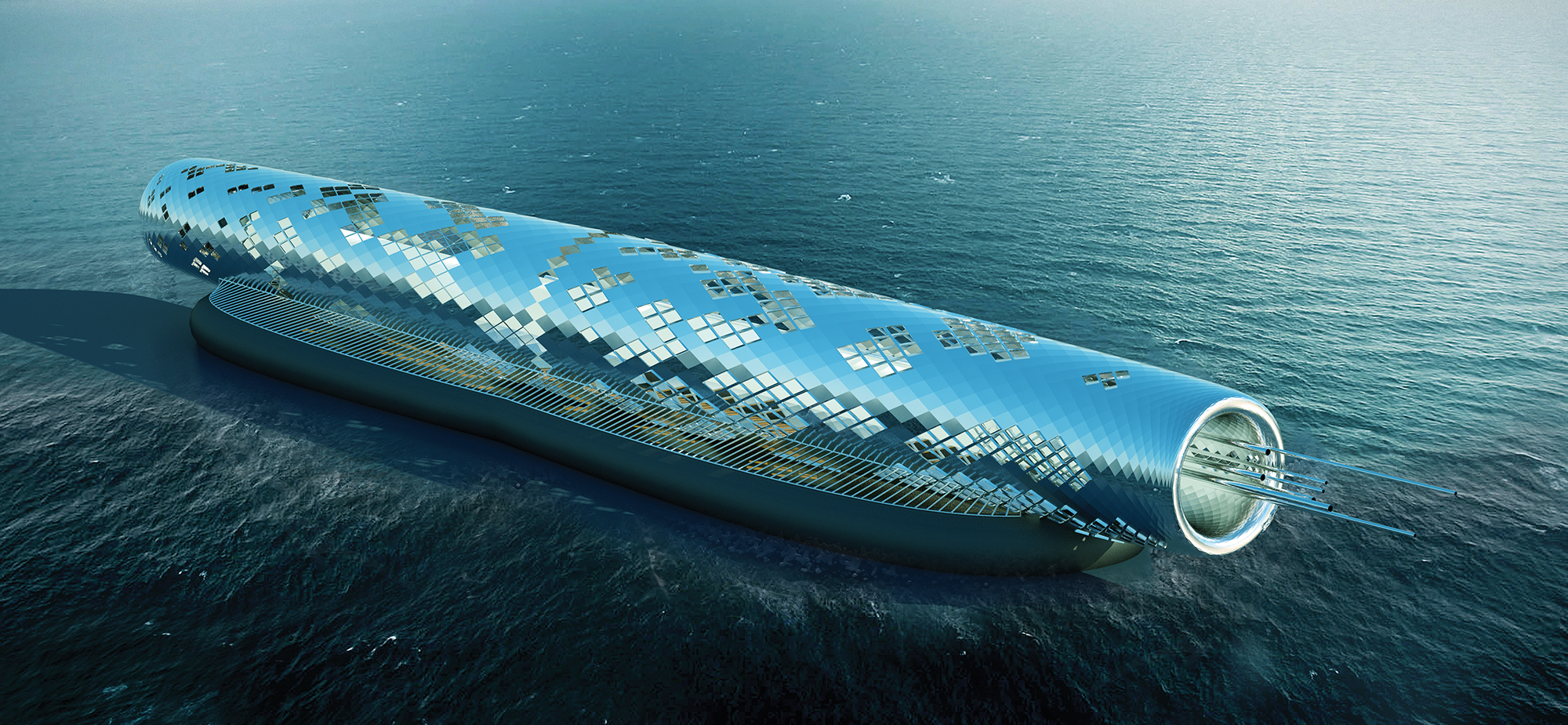
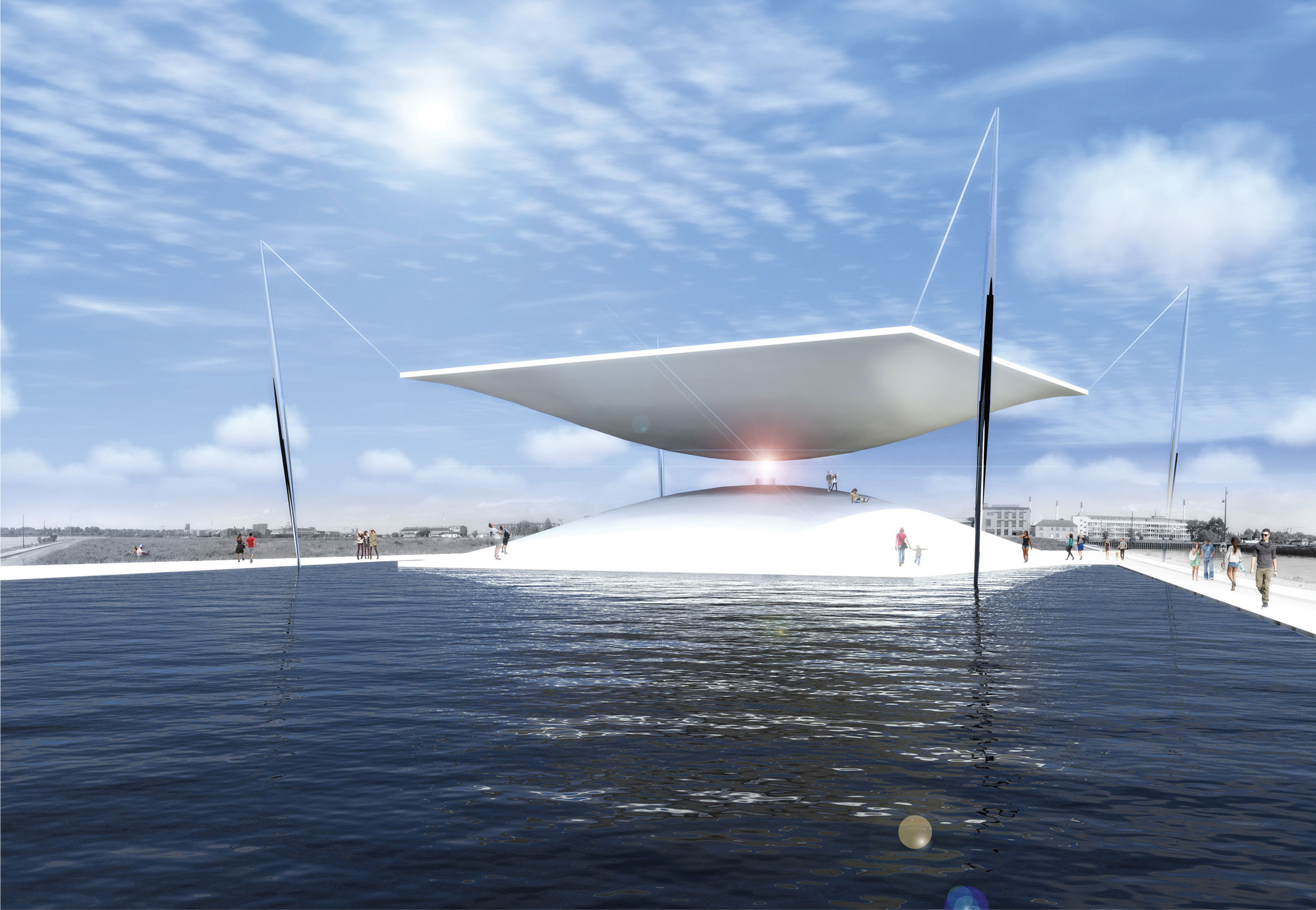











Solar Hourglass, 1st Place Winner LAGI 2014 Copenhagen
Santiago Muros Cortés
Energy Technologies: concentrated solar power (thermal beam-down tower with heliostats)
Annual Capacity: 7,500 MWh
Arch of Time by Riccardo Mariano incorporates solar photovoltaic modules to generate 400 MWh per year.
It is being built in Houston and will offset the electricity demand of the surrounding neighborhood. Learn more.
Light Up, 1st Place Winner, LAGI 2018 Melbourne
Martin Heide, Dean Boothroyd, Emily Van Monger, David Allouf, Takasumi Inoue, Liam Oxlade, Michael Strack, Richard Le (NH Architecture);
Mike Rainbow, Jan Talacko (Ark Resources); John Bahoric (John Bahoric Design); Bryan Chung, Chea Yuen Yeow Chong,
Anna Lee, Amelie Noren (RMIT Architecture Students)
Energy Technologies: flexible mono-crystalline silicon photovoltaic, wind energy harvesting, microbial fuel cells
Annual Capacity: 2,220 MWh
Lodgers, top submission to LAGI 2020 Fly Ranch
By Zhicheng Xu and Mengqi Moon He
brings together composting toilets, reclaimed timber waste, traditional thatching methods using local materials, computational
script-generated parametric design, and native species shelters to provide an environmental education venue, soil replenishment,
sustainable waste management, and habitat enrichment for Fly Ranch
Starlit Stratus, 1st Place Winner, LAGI 2019 Abu Dhabi
TEAM: Sunggi Park
ENERGY TECHNOLOGIES: solar photovoltaic, water harvesting with hygroscopic materials
ANNUAL CAPACITY: 2,484 MWh
Beyond the Wave, a submission to LAGI 2014 Copenhagen
Jaesik Lim, Ahyoung Lee, Sunpil Choi, Dohyoung Kim, Hoeyoung Jung, Jaeyeol Kim, Hansaem Kim (Heerim Architects & Planners)
Energy Technologies: organic thin film
Annual Capacity: 4,229 MWh
The LAGI 2018 Melbourne publication features 65 submissions to the LAGI 2018 design challenge and essays by Jodi Newcombe,
Andrew Dana Hudson, and David Helms. Designed by Schifino Design. Learn more about our publications here >
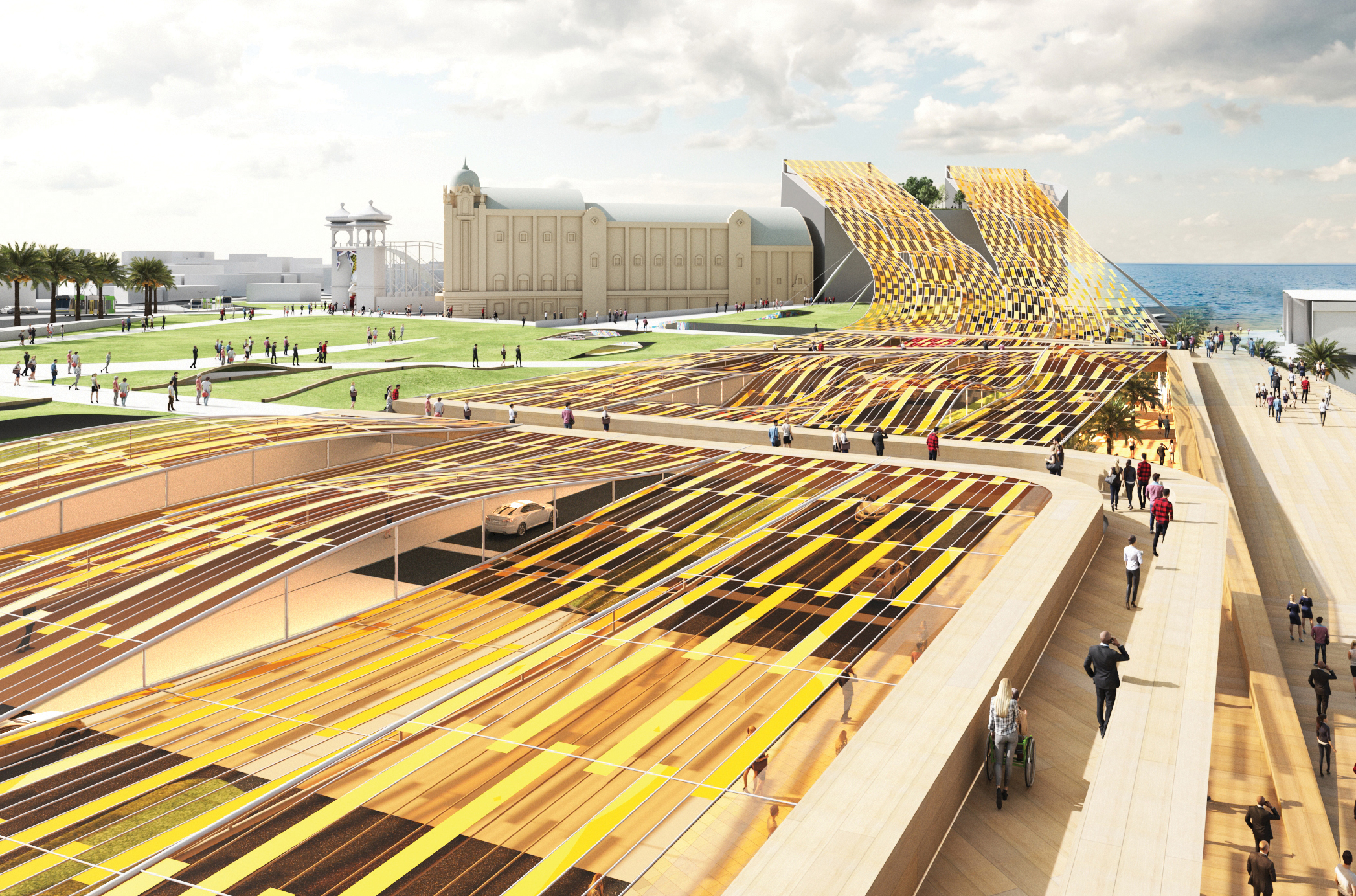
The Pipe, Shortlisted Submission, LAGI 2016 Santa Monica
Abdolaziz Khalili, Puya Kalili, Laleh Javaheri, Iman Khalili, Kathy Kiany (Khalili Engineers)
Energy Technologies: Photovoltaic Panels
Water Harvesting Technologies: Electromagnetic Desalination
Annual Capacity: 10,000 MWh to generate 4.5 billion liters of drinking water
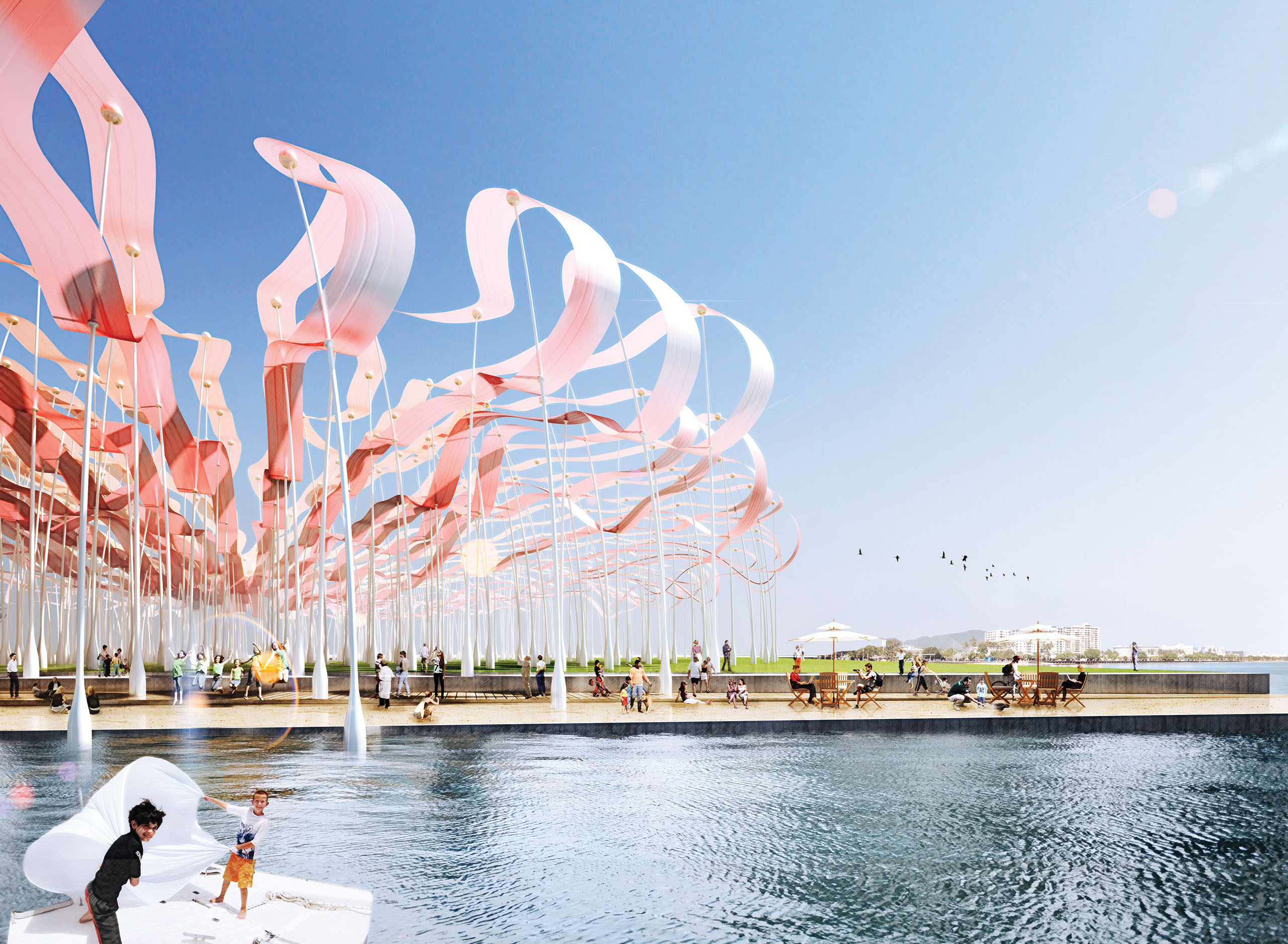
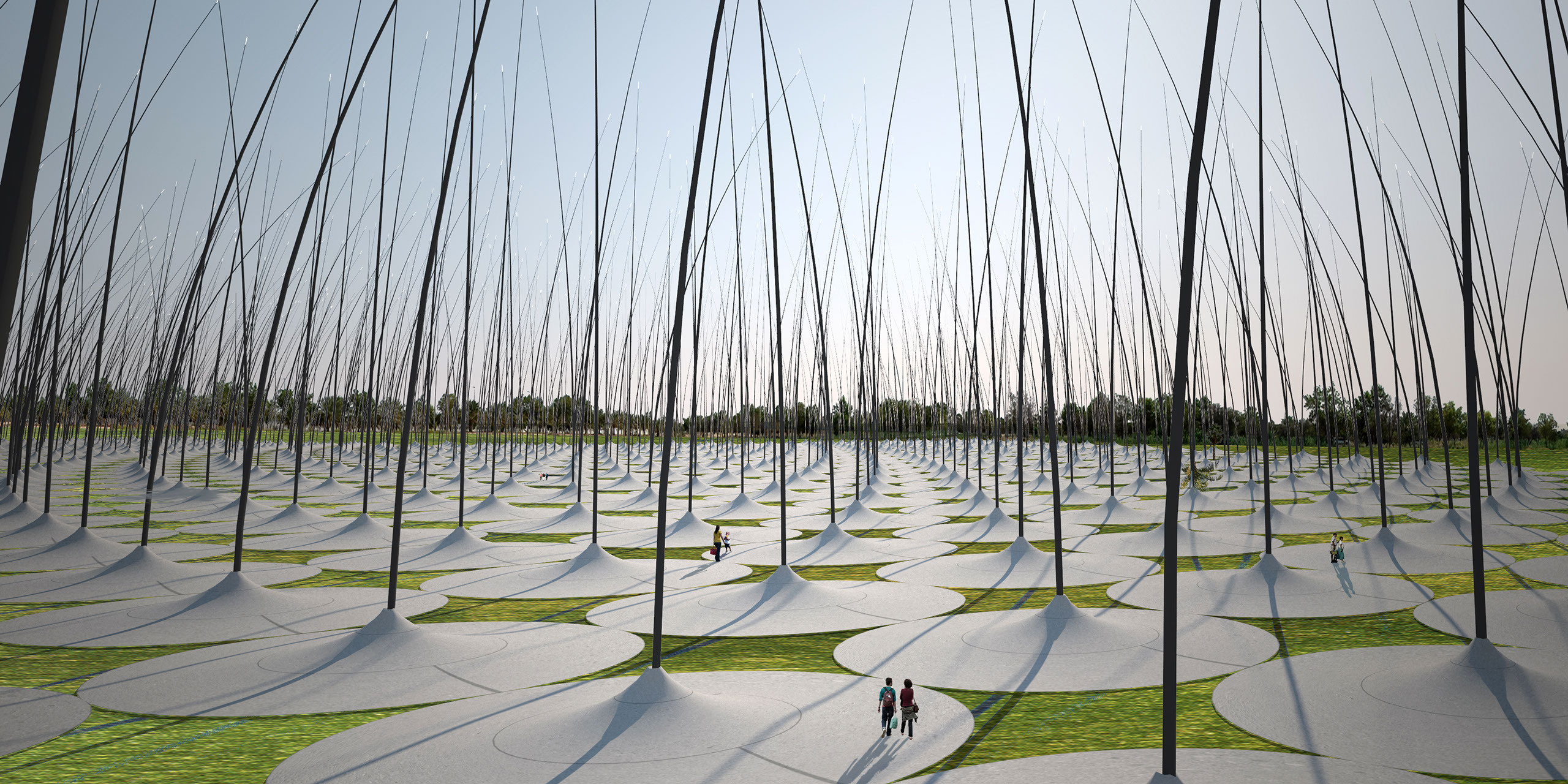
Windstalk, a submission to LAGI 2010 Dubai/Abu Dhabi
Darío Núñez Ameni and Thomas Siegl, with Atelier dna
Energy Technologies: piezoelectric discs, linear alternator
Annual Capacity: 20,000 MWh
Energy Duck, a submission to LAGI 2014 Copenhagen
Hareth Pochee, Adam Khan, Louis Leger, Patrick Fryer
Energy Technologies: photovoltaic panels, hydraulic turbines
Annual Capacity: 400 MWh
Solar Eco System, a submission to LAGI 2010 Dubai/Abu Dhabi
Antonio Maccà, Flavio Masi
Energy Technologies: photovoltaic panels
Annual Capacity: 1,000 MWh
Art+Energy Camp, Summer 2015, Pittsburgh
This unique six-week summer (2015) camp in the Homewood neighborhood of
Pittsburgh gave 20 kids an education in energy science, climate science, art, design,
and solar power installation. The final outcome was a built solar artwork—Renaissance
Gate—designed by the campers! Learn more
<
>
The Land Art Generator engages the public in the co-design of our clean energy future, bringing together the disciplines of public art, urban planning, creative placemaking, renewable energy, and environmental justice.
We provide context-specific and culturally-relevant design solutions for distributed clean energy that reflect the needs of local communities through design competitions, direct commissions, calls for proposals, Solar Mural artworks, and participatory co-design projects for people of all ages.
Any creative placemaking opportunity can also be a climate solution.
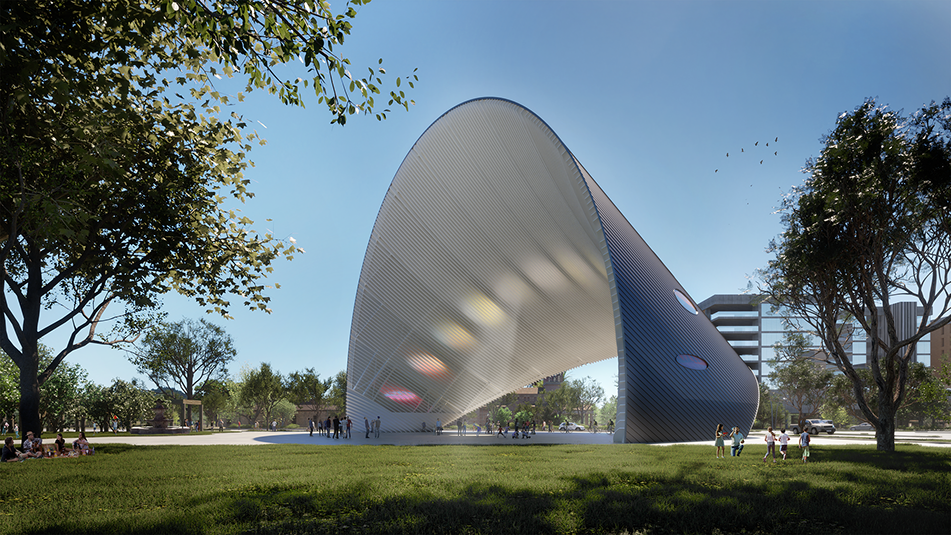

Arch of Time by Riccardo Mariano incorporates solar photovoltaic modules to generate 400 MWh per year, offsetting the electricity demand of the surrounding neighborhood. It is the first public artwork in the world designed to be a net positive contribution to the climate crisis. By generously providing clean energy to the city, the arch will inspire the public about the beauty and wonder of a post-carbon future, while providing an exceptional venue. Learn more
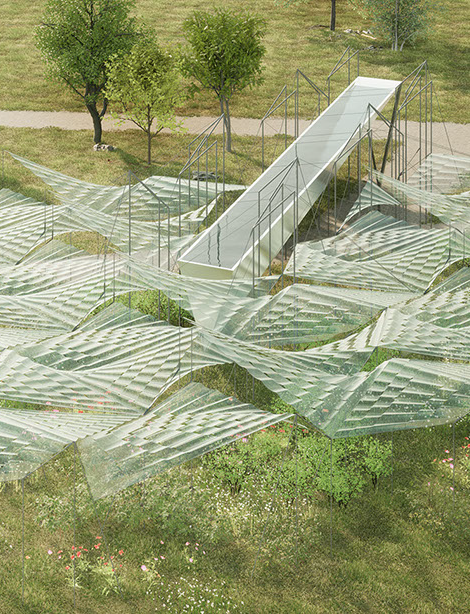
Plane of Water by Zsuzsa Péter incorporates organic photovoltaic (OPV) solar to generate 40 MWh each year. The artwork provides additional social co-benefits including shaded public space, water harvesting, and urban gardens. A shortlisted entry to the Land Art Generator Initiative 2022 (LAGI 2022) design competition for Mannheim in partnership with BUGA 23.
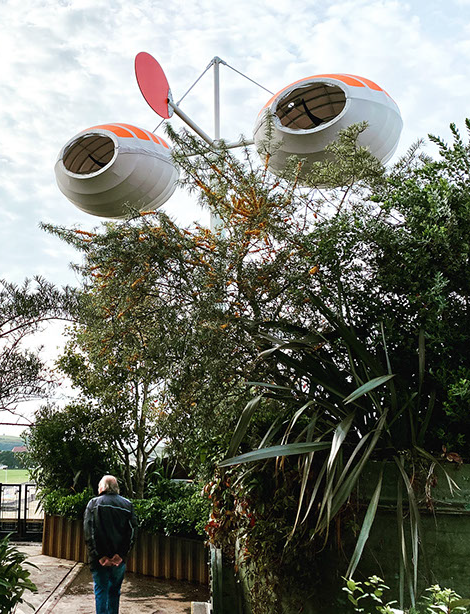
WindNest by Trevor Lee incorporates compact acceleration wind turbines and thin film solar
to generate an annual capacity of 30 MWh.
The submission to the Land Art Generator Initiative 2010 design competition for Abu Dhabi (LAGI 2010) was
re-imagined and constructed full-scale for SEE MONSTER, a part of the UNBOXED UK Festival in 2022.
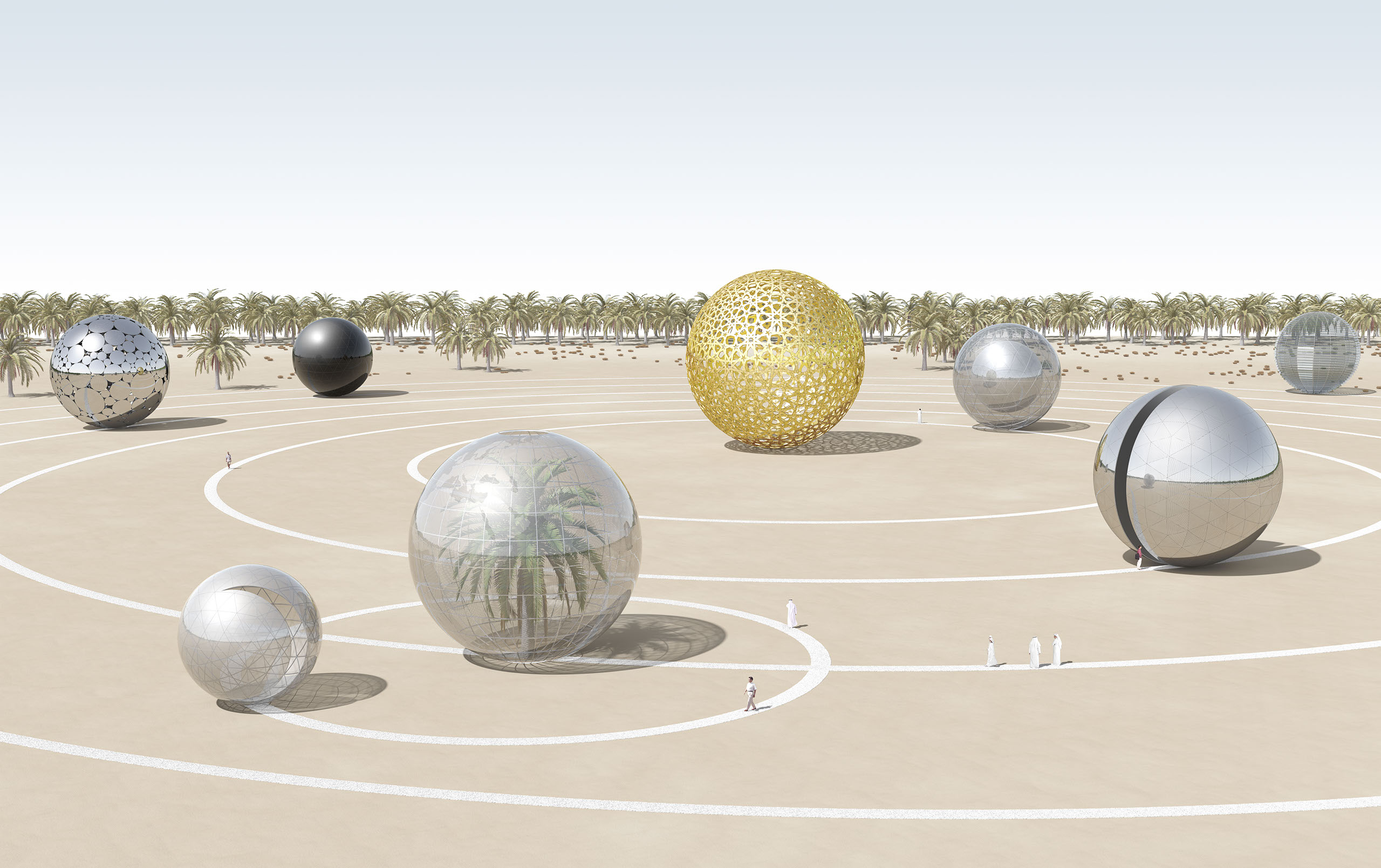
International open-call competitions for the UAE, New York City, Copenhagen, Santa Monica, Melbourne, Abu Dhabi, Fly Ranch, and Mannheim have resulted in over 1,500 designs from creative teams across more than eighty countries.
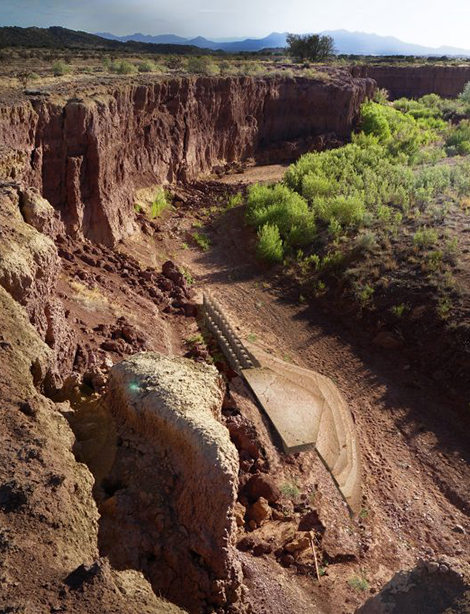
MEAnder by Ryan Henel and Craig Sponholtz is the chosen design from the LAGI-MEA invited design competition for the Modern Elder Academy’s regenerative ranch, Saddleback, south of Santa Fe, New Mexico. Images courtesy of the artist team (rendering by Ryan Bromberg). MEAnder will be implemented on site in 2023.








